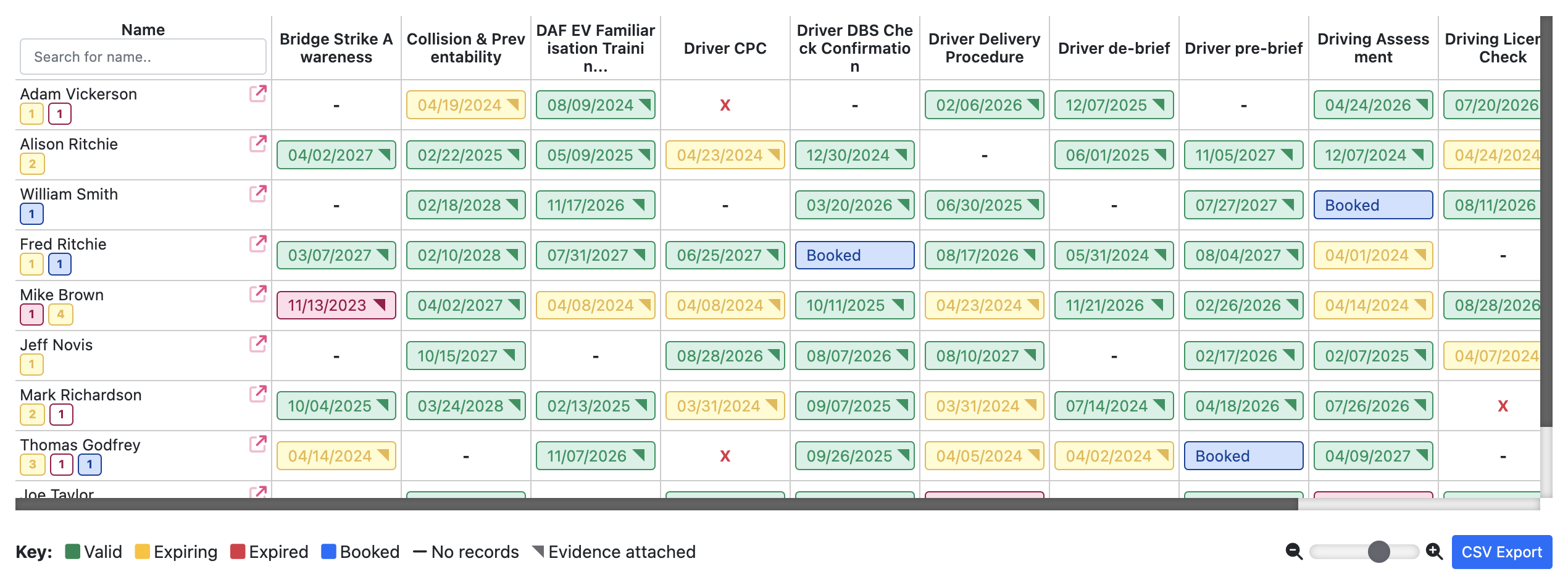
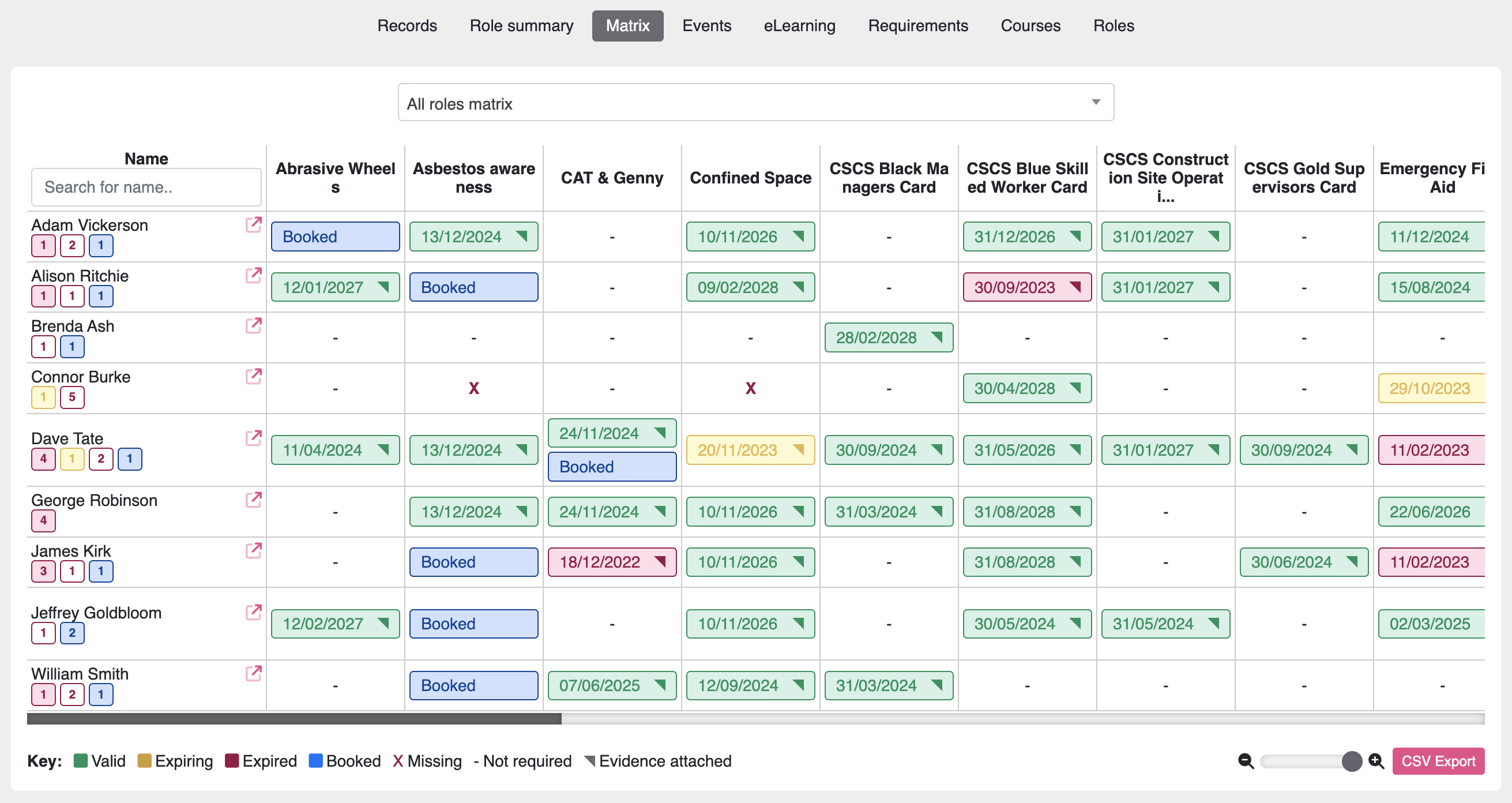
It’s as important as ever for employers to have a clear understanding of their workforce skills and abilities, this is where a skills audit comes in.
In this quick guide, we’ll explore what it is, why it’s important, and how to conduct one effectively.
What is a Skills Audit?
A skills audit is a systematic process of identifying, assessing, and documenting the skills and competencies of an individual or a group of individuals. It involves evaluating both technical and soft skills, as well as identifying any gaps in skills and knowledge.
The audit can be conducted for various purposes, such as career development, performance evaluation, or workforce planning. It can be done at an individual level or at an organisational level.
Why is a Skills Audit Important?
The process is important for both individuals and organisations. Here are some reasons why:
- Identify strengths and weaknesses: A skills audit helps individuals and organisations to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This information can be used to make informed decisions about training, career development, and recruitment.
- Plan for the future: By understanding the skills and competencies of their workforce, organisations can plan for future needs and identify any skills gaps that need to be addressed.
- Improve performance: The audit can help individuals and organisations to improve their performance by identifying areas for improvement and providing a roadmap for development.
- Stay competitive: In today’s fast-paced job market, it’s important for individuals and organisations to stay competitive. A skills audit can help identify areas where individuals or organisations may be falling behind and take steps to stay ahead.
How do I conduct a Skills Audit?
Conducting the audit involves several steps. Here’s a quick guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope
The first step in conducting the audit is to define the purpose and scope of the audit. This will help you determine what skills and competencies you need to assess and who will be involved in the process.
Step 2: Identify the Skills and Competencies to be Assessed
Next, you’ll need to identify the skills and competencies that are relevant to the purpose and scope of the audit. This may include technical skills, soft skills, and industry-specific skills.
Step 3: Choose an Assessment Method
There are various methods that can be used to assess skills and competencies, such as self-assessment, peer assessment, or manager assessment. Choose the method that best suits your needs and resources.
Step 4: Gather Data
Once you have identified the skills and competencies to be assessed and chosen an assessment method, it’s time to gather data. This can be done through surveys, interviews, or performance evaluations.
Step 5: Analyse the Data
After gathering the data, it’s important to analyse it to identify any skills gaps or areas for improvement. This will help you make informed decisions about training, career development, and recruitment.
Step 6: Create an Action Plan
Based on the results of the audit, create an action plan to address any skills gaps or areas for improvement. This may include training programs, mentoring, or recruitment strategies.
Step 7: Review and Update Regularly
A skills audit is not a one-time process. It’s important to review and update it regularly to ensure that the skills and competencies of individuals or the workforce are aligned with the needs of the organisation.
Tools for Conducting a Skills Audit
There are various tools available to help individuals and organisations conduct a skills audit. Here are some popular options:
Skills Inventory
A skills inventory is a database that contains information about the skills and competencies of individuals or a workforce. It can be used to track skills, identify gaps, and plan for future needs.
Competency Frameworks
Competency frameworks are a set of skills and behaviours that are required for a specific role or job. They can be used to assess skills and competencies and identify areas for development.
Online Skills Assessment Tools
There are many online tools available that can help individuals and organisations assess their skills and competencies. These tools often provide personalised feedback and recommendations for improvement.
Software such as moralbox.com contain tools to perform an effective audit: https://www.moralbox.com/software/workforce-manager-training-matrix/
Conclusion
A skills audit is an important process for individuals and organisations to identify strengths and weaknesses, plan for the future, and improve performance. By following the steps outlined in this guide and using the right tools, you can conduct a successful skills audit and stay ahead in today’s competitive job market.
Further Reading
- Robert Half – How to conduct a skills audit with your employees: This article provides a comprehensive guide on conducting a skills audit, highlighting its importance in assessing employee skills and identifying knowledge gaps for better workforce management. Read more.
- Journal of Accountancy – 5 steps for conducting a personal skills audit: This article presents a focused approach on conducting a personal skills audit, emphasizing the importance of self-awareness and continuous improvement in professional development. Learn more at the Journal of Accountancy.
- Inside.6Q – How to Conduct a Skills Audit: This article emphasizes the importance of assessing professional skills during the recruitment process and for optimizing a company’s performance. It suggests a structured approach to skills audits and offers tips on using technology effectively in HR work. Explore more.
- The Human Capital Hub – Skills Audit: The necessary steps in a Skills Audit: This article discusses the process of conducting a skills audit and highlights common mistakes to avoid. It delves into the importance of aligning the audit with business objectives and provides insights on various methods for assessing different types of competencies. Learn more.

Alison is the Moralbox Customer Success Manager. She ensures that our customers enjoy the benefits and get the very best experience out of our products. Alison has over 8 years experience as a training manager.